How Antioxidants Work to Protect Your Health-A Comprehensive Review of Their Benefits
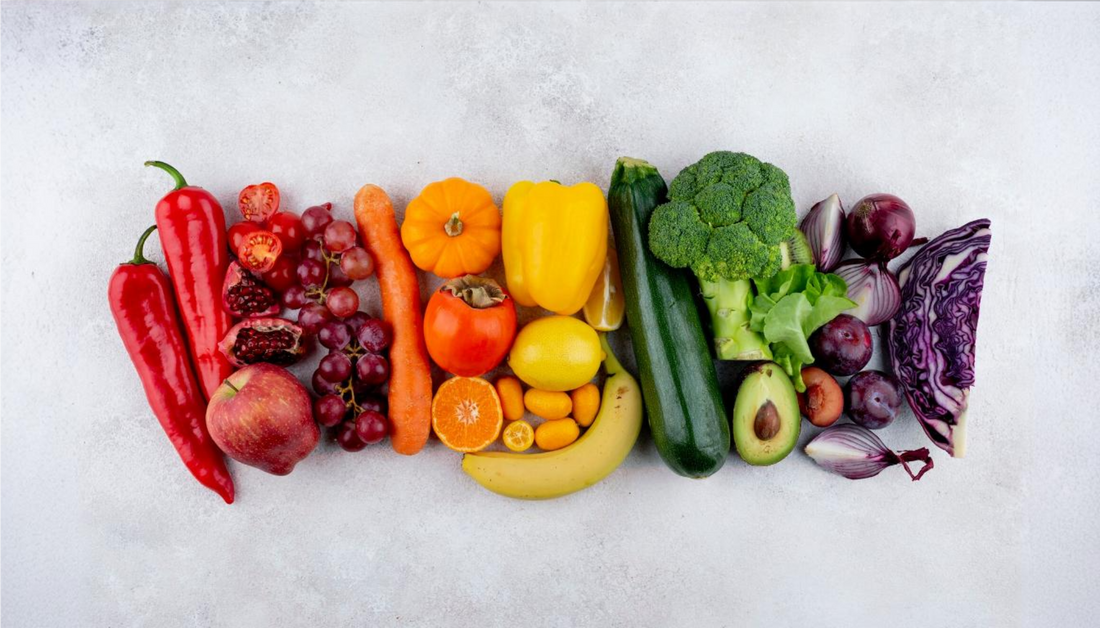

Nature's Medicine for a Healthier Life: Antioxidants In recent years, The human body continually fights against infections and diseases, but also is acted upon by environmental influences like tobacco usage, air pollution, and sun exposure, all of which produce free radicals that destroy healthy cells. Free radicals' oxidative stress has increasingly been linked with many diseases that cause cancer, heart disease, and aging. We will learn how important antioxidants are for the prevention of illness, retardation of age, and general wellbeing by examining how they avoid negative consequences.
Introduction
The free radicals are unstable atoms that accelerate aging and cause chronic illnesses such as cancer and cardiovascular diseases through the process of oxidative stress, which antioxidants neutralize. Their abundance of fruits and vegetables, together with numerous different teas, provide the body with a natural defense against chronic illnesses. Nature is giving the key to health and endurance to people through antioxidants.Oxygen is required for life, but its utilization in cellular energy synthesis produces free radicals, mostly reactive oxygen and reactive species of nitrogen. While modest quantities of these species can enhance cellular responses and immunological function, large levels cause oxidative stress, which leads to chronic illnesses such as cancer and cardiovascular disease.
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants are substances which help protect the body from free radicals, unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress, and a host of other health problems and situations including aging and chronic diseases such as cancer or heart disease. It neutralizes these causative and destructive molecules therefore reducing cellular destruction enhancing the immune system, and generally well-being.
Reactive oxygen species are produced both inside and outside the body through sources such as smoking and pollution, which causes inflammation in the body if not checked in the body. Such antioxidants include vitamins C and E, selenium, and plant chemicals known as flavonoids, in such foods as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and teas. Antioxidants "scavenge" free radicals, defend cells against damage, reduce inflammation, and play a part in protecting health.
Importance in combating oxidative stress
Oxidative stress is the condition with a loss of balance between antioxidant defenses and formation of ROS. ROS represent the natural by-products of oxygen metabolism, though the increase in production is a feature of environmental stress conditions like UV radiation, toxins, and certain drugs.
- It produces cellular and tissue damage, and it is implicated in a variety of diseases, such as diabetes.
- Some of the antioxidants reverse oxidative stress by containing vitamins E, flavonoids, and polyphenols.
- Oxidative stress is essentially pathological but could be put to specific targeted use to kill particular types of cancer cells.
- Antioxidant levels in blood plasma can help estimate oxidative stress and potentially harmful effects on health.
Blood plasma antioxidant levels can be used as predictive indicators for oxidative stress and possibly for its devastating health effects.
Analysis of the Different Types of Antioxidants and their Health Benefits
Based on their origins and physiological functions, antioxidants are grouped.
- Two types of antioxidants can be easily differentiated : enzymatic including those that are produced in the body, such as superoxide dismutase, and nonenzymatic, which contains vitamins C and E and minerals such as selenium that are found in food.
- An endogenous antioxidant is glutathione that occurs naturally within the body. BHT and all other chemical food preservatives are synthetic antioxidants.
- Finally, meals rich in hormetic antioxidants, such as the very potent herb turmeric, are critical to stimulating the body's defenses. Adaptive responses are assisted by antioxidants that bring about stress management and defense against damage in the body.
Major Nutrients: Vitamin C and Vitamin E Antioxidant and Selenium in Health:
These antioxidants work to counteract the natural oxidative stress in the body.They can be produced in the body or taken in through diet and tablets intake.- As an antioxidant, vitamin C preserves damaging free radicals and unstable chemicals from damaging the cells. It promotes collagen synthesis, thus hastening healing and improving the immune system. The skin would thus be bright and healthy.
- Meanwhile, Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that protects the cells from oxidative damage. It can be found in seeds, nuts, vegetable oils such as sunflower oil, and different leafy greens.
- Selenium: Concentrations of selenium in foods depend more upon the conditions of the soil and water environment. Primarily from foods such as rice, corn, wheat, and other whole grains, nuts, eggs, cheese, and legumes.
- The human body might use such compounds to offer as much protection as required, just like vitamins and minerals that were necessary for the maintenance of life.
Phytochemicals and Their Sources: Important Nutrients for Health and Nutrition
Phytochemicals are natural defenses by plants, fruits, vegetables, beans, and grains against viruses, bacteria, fungi, and insects.
- They also act as a kind of protective shield over human cells, shielding them from damage induced by toxic contaminants in the environment and byproducts of normal metabolism.
- It has antioxidant capabilities that could neutralize free radicals, which damage DNA and thus cause diseases, according to a physician nutrition specialist with UCLA Health.
- These include flavonoids found in berries and tea. Carotenoids found in carrots and spinach.
- Glucosinolates found in cruciferous vegetables may reduce the risk of cancer in people; saponins in beans could contribute towards lowering cholesterol.
- Lignans in the flaxseed and phenolic acids in coffee and fruits, cloves, and dark chocolate balance hormones and reduce inflammatory conditions. The adequate intake of colorful fruits and vegetables guarantees an appropriate amount of these beneficial phytochemicals that ensure general well-being and health.
The function of antioxidants like this is vital for counteracting the oxidative stress impact on the body, which contributes to the promotion of longevity and the enhancement of immune functions.
Antioxidants and General Health Health Benefits
Eating antioxidants is healthy for your body in general.
lowering India's risk of chronic illnesses
- Eye Health: More recently, studies have also looked into antioxidant eyes health connections and found that irreversible vision loss is most commonly associated with conditions that affect people older than 50.
- Maintain fitness and proper weight. The risk of developing diseases such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes would be very slim.
- Handle stress: To preserve general wellbeing, practice stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness and relaxation.
- Prevention of Cancer: Although it was well established that antioxidants protect the human body against oxidative free radicals and perhaps cancer, scientific evidence till date is not seen of antioxidant supplements preventing cancer.
- AMD develops when the macula at the back of the eye deteriorates until complete loss of central vision takes place over time and the focus should be on antioxidants and proper eye health.
Further research is needed to be completed in order to understand completely how food-extracted antioxidants contribute to reducing risk factors of developing cancer.
Antioxidants Benefits for Skin health and aging:
- Vitamin C Benefits Applying vitamin C to the skin tends to make the skin improve its texture and the outlook of wrinkles and lines and avoid damage that the sun could inflict on the skin as well as diminish dark spots appearance.
- Vitamin E: Healthy skin is a result of an antioxidant diet, by which means a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, and oily fish.
Further Research: While there is some confirmation that vitamins C and E provide skin advantages, more research is needed to fully understand how well they work.
Include antioxidant-rich foods into your diet
One of the simplest and most effective ways to enhance antioxidant levels from diets in India while using dietary supplements is an adequate nutrient-dense diet with high amounts of fruits and vegetables.
- All the above superfoods, including spinach, berries, and apples, should be included in almost all one's meals.
- Along with this, for a healthy dose of antioxidants with some beneficial fats, include nuts like walnuts and almonds, and seeds like chia and flax seeds in your diet.
- Add legumes that are: Beans with your meal, lentil, chickpea would provide the protein component that will contribute to your taking in of antioxidants.
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa will store a lot of antioxidants and fibers.
- Herbs and Peppers Use: Add herbs and spices to your meal, containing antioxidants in turmeric and garlic.
Processed foods and Sugary snacks avoid them because they are low in antioxidant absorption.
Foods rich in antioxidants
- Lycopene is mainly found in red and pink fruits and vegetables such as watermelons, papaya fruit, pinkish grapefruits, and tomatoes. In normal circumstances, the richest sources of lycopene in diets are tomato-based products.
- Compounds present in several orange-colored foods. These include carrots, sweet potatoes, squash, pumpkin, and apricots. It is also seen in leafy greens like kale, spinach, and collard greens containing lutein.
- A number of fruits and vegetables, along with poultry, meat, fish, and even fortified cereals, contain vitamin C.
- Almonds, broccoli, mangoes, and other foods that include corn, soybean, and sunflower oil are all forms of food that contain vitamin E.
- Berries consisted of blackberries, wild strawberries, cranberry fruits.
- Coffee gives you the superfood benefit with the amount of caffeine. This will prevent you from getting jitters and crashes that come with traditional coffee.
Another thing, supplements lack the balance, which is always found in food. For example, natural vitamin E in foods has eight forms, whereas a majority of supplements have a single form. Some antioxidants have become poisonous in substantial quantities. Before using antioxidant tablets, kindly see your healthcare provider; especially pregnant and breastfeeding moms.
Conclusion
This free radical scavenging ability neutralizes them in order to reduce oxidative stress, so that antioxidants are crucially important for your health. All these sources from fruit and vegetables to nuts and whole grains offer health benefits from reducing the risk of diseases to enhanced immune functions. In India, these supplements can provide more of these nutrients, but they cannot replace some of the overall benefits derived from a balanced diet. All these nutrient-dense foods would add up to your daily diet and help generally towards health and energy.FAQ’s:
1. How do the body's antioxidants function?By lessening oxidative cell damage, it neutralizes and stabilizes free radicals. By giving electrons and initiating repair processes, they preserve cellular health generally and guard against illnesses that are classified as chronic.
2. Can a diet alone provide sufficient antioxidant intake?
Antioxidants can be adequately supplemented by a diet rich in whole grains, nuts, seeds, and bright fruits and vegetables. Reduced oxidative stress, and general well-being, are achieved through consumption of an assortment of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants from food items, as aforementioned.
3. What are the best antioxidant tablets?
Since these prevent oxidative stress, the best antioxidant tablets are vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium. Always see a doctor before taking a supplement.
No comments





















0 comments