Sweet Addiction: How Sugar Influences Mental Health, Mood, and Cognitive Function
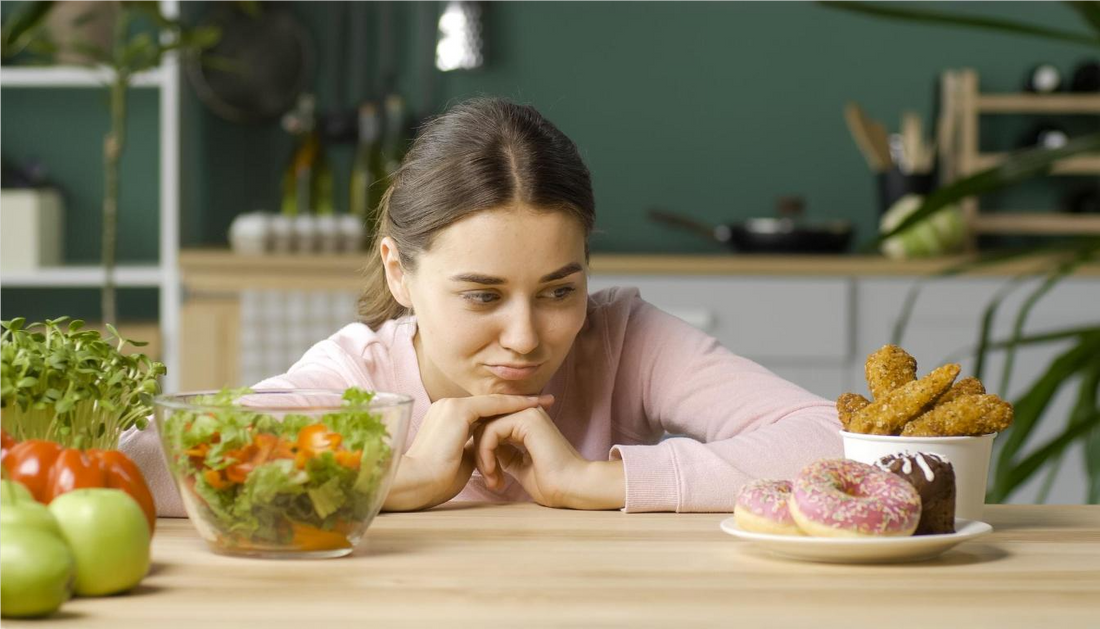

Chocolates, sweets, laddus... yummyy! Most people love these kinds of sweets, but eating too many sugar-laden items can affect your health and skin. Today, we explore how excessive sugar intake can disrupt mood, increase anxiety, and affect the cognitive abilities. The Dia Control supplement best for diabetes management in terms of handling blood sugar levels and assisting glucose metabolism is supportive in promoting health overall. These reduce sugar cravings and maintain stable energy levels very effectively. The guide also delves into the complex relationship between sugar and mental health, exploring the impact of sugar on the brain and helps you to understand this sweet addiction's effects.
What Is the Impact of Sugar on Mental Health? Current Research Insights
Interest in the impact of sugar on mental health has increased over the past few years. Research studies indicate that high consumption of sugar is related to mood and cognitive performance in different ways.
Key insights from the current research are presented here:
1. Mood Swings and Irritability: Blood sugar swings from ingesting large amounts of sugar, especially refined sugars, have been linked to mood swings, irritation, and depressive or anxious feelings. Rapid blood sugar elevations and drops could send brain chemistry into a downturn.
2. Higher Incidence of Anxiety and Depression: Recent findings have further revealed that diet rich in processed foods and high sugar consumption is a predisposing risk for mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. This could be due to sugar's impact on inflammation, which would translate into the altered activity in the brain and loss of emotional regulation.
3. Mental Condition: There may be a negative effect of mental performance due to excessive sugar consumption. It is believed to affect the region of the brain known as the hippocampus, which controls memory and the learning process. This is the reason that this problem is associated with memorization disorders and lack of concentration.
4. The Gut-Brain Level: New research indicates sugar can actually alter gut microbiota, which is significant for mental well-being. Imbalances in gut flora are associated with anxiety, depression, and other problems related to mood.
5. Brain Protection and Inflammation: Chronic sugar intake can lead to inflammation within the entire body as well as in the brain. Inflammation can impede the healing and protects the brain and has been associated with several mental disorders, including depression.
From mood swings to cognitive decline, the effects of excess sugar are profound. Reduced sugar intake will bring about improvements in emotional and mental wellbeing, thereby creating a healthier body and mind.
Overview of sugar consumption and mental health
The significant impact of sugar intake to one's mental health has been seen as altered mood, cognitive abilities, and emotional states according to several studies. The major points are given below:
1. Mood swings: With tremendous highs and lows in blood sugar, sugar can fuel irritability, anxiety, and mood swings. Over time, this rollercoaster may build up to induce more chronic feelings of depression.
2. Brain Performance: Over the long term, a diet that contains too much sugar leads to decreased memory, attention, and general cognitive ability. Too much sugar is said to cause the inflammation in the brain responsible for mental disorders like depression and anxiety.
3. Hormonal imbalance: Sugar affects the secretion of sensitive hormones; for example, insulin and cortisol, which regulate energy and stress respectively.
4. High consumption of sugar over long periods results in high cortisol levels; this worsens anxiety and stress conditions and makes it almost impossible to manage emotions.
5. Sugar evokes craving and compulsive consumption because the brain reacts to it similarly as it does to addictive substances. It can perpetuate overeating, eventually making the emotional equation keep turning around with possible reliance on sweet food items to stabilize mood.
6. Gut Health and Psychological Health: Overall psychological health is affected by gut microbiota. A diet high in sugar tends to disturb it. Mental issues connected with imbalances of gut flora include anxiety and sadness.
7. Long-term effects on mental health include the possibility of chronic depression, impairment of cognitive function, and even a propensity for developing Alzheimer's disease in people who have a tendency to consume large amounts of sugar. Cutting sugars may lead to improved brain functioning and mood.
The negative impacts of the widespread ingestion of excess sugar include mood swings, cognitive decline, increased stress, and much more, which impact mental health negatively. Reducing sugar can strengthen emotional stability as well as the function of the brain.
What's the science behind sugar and mood?
A link to the sugar and mood basically has to do with how sugar interacts with the brain and body. Here is how it works:
- The brain Inflammation: Diets high in sugars have been shown to produce more brain inflammation, linked with mood disorders such as anxiety and depression as well as impairments in cognitive function. Chronic inflammation may further compromise the integrity of mood management and balance in the brain.
- Interaction between stomach and brain: A patient's diet has an impact on the gut microbiota that has very high influences on mental health. The balance of gut bacteria could become upset by a sugary diet affecting, for instance, the production of mood-regulating neurotransmitters like serotonin. Anxiety or depression can be worsened in this case.
- Effects on Hormones: Consuming sugar increases the production of insulin, which works to regulate blood sugar. Repeated consumption of sugar may lead to a resistance buildup, which can alter mood- regulating chemicals, including cortisol, and affect metabolism. This could enhance tension and anxiousness.
- Blood Sugar Levels: When you consume it, your body's blood sugar levels goes up, and you instantly have that boost of energy.
- Brain The mechanism: The brain uses to release dopamine is activated by sugar. It's called the "feel good" neurotransmitter. Though this will give temporary satisfaction, it becomes a cycle of craving, with the brain seeking more sugar to produce that feel-good feeling. Eventually this induces dependence and results in sugar-induced mood dips as the levels drop.
Intake of fruit, green leafy vegetables, and high-fiber, low-GI food is associated with reduced risk of diabetes, although protective factors like fiber and exercise are not yet fully considered. Some fats, particularly from dairy, may confer some protection, but diets excessively high in fat are not recommended because of potential obesity. Long-term studies on the relation of macronutrient intake, exercise, and sugar's more specific effects are needed. [1] [2] [3]
How does sugar affect brain chemistry?
Sugar changes brain chemistry for neurotransmitters, hormones, and other neural pathways. Here's why:
1. Dopamine Release: Sugar stimulates the brain's reward system, releasing dopamine associated with pleasure and reward, which can create a sense of temporary "high" but leads the brain to compensate through continuous consumption over time to achieve the same effect-coveted by cravings and dependency.
2. Serotonin Levels: Sugar consumption temporarily calms one down because it elevates serotonin, the neurotransmitter known as the "feel-good." But when the brain cannot manage this naturally, repeated reliance on sugar for serotonin may lead to mood swings and depression.
3. Stress hormones: Intake of a high amount of sugar triggers the stress hormone cortisol, especially in the case of blood sugar spikes. It may raise levels of stress and anxiety.
4. Chronic consumption of sugars creates inflammation in the brain, a chronic established connection with mental disorders, such as anxiety and depression, and impaired cognitive function.
5. Blood Sugar Levels and Brain Activity: A diet rich in sugars causes a quick increase followed by a sharp fall in blood sugar levels, resulting in unstable energy supply in the brain and thus affects emotional balance, memory, and concentration.
To get an understanding of this, refer to this article “The Impact of Sugar on Your Health”. Of course, it will clear all your doubts.
What Sugar Reduction Options Are Effective?
Overall health and wellbeing can be significantly improved by reducing sugar intake. The following are some effective strategies:
1. Prepare at Home: Preparing in the home, one is totally in control of whatever ingredients one incorporates. Added sugars can be avoided from sauces, or snacks.
2. Reduce soda: Swap soda and other sugary drinks, such as energy drinks, with water, herbal teas, or unsweetened juices.
3. Avoid artificial sugars as they tend to alter your taste, and they increase appetites for sugary meals even though they may lower caloric consumption.
4. Pick Your Snacks Wisely: Choose nutrient-dense snacks such as fruits, nuts, seeds, or milk products rather than candy, cookies, and baked goods.
5. Consider Healthy Foods: Choose foods such as whole grains, fruits and vegetables, and healthy meats that will contain less added sugar.
6. Study labels of food products: Observe the lists of ingredients in processed food for hidden sugars. Look out for words like maltose, fructose, sucrose, and corn syrup.
7. Select only natural sugars: When adding sweet flavours to food, use fruits, honey, or maple syrup sparingly.
The link between sugar and mood remains unclear, with inconsistent findings often focusing on short-term effects after fasting or glucose intake. Hypoglycemia is found to negatively affect mood and cognition and complicates studies as it can be temporarily improved by any carbohydrate intake.
Practical Tips for a Low-Sugar Lifestyle
Making thoughtful food choices such as giving priority to whole foods and cutting less on processed sugary foods is part of living a low-sugar lifestyle.
- Plan Your Meals: To avoid rash, sugary decisions, chart out your meal planning for the week, focusing on full, unadulterated meals.
- Start by having breakfast: Instead of sugary cereals or pastries for breakfast, include low sugars, high proteins, Greek yogurt, eggs, or oatmeal with fresh fruit on top.
- Drink Water: Replaces sugary beverages with water, herbal teas, or sparkling water that has a slice of cucumber or lemon incorporated.
- Choose Your Snacks Wisely: To curb cravings, have low sugar, healthy snacks on hand, such as fresh fruit, hummus-topped vegetables, almonds, and seeds.
- Select Natural Sugars: When a hint of sweetness is needed, add them in small amounts, honey, maple syrup, and dates.
- Concentrate on Fiber: In order to control the balance of blood sugar and to reduce hunger, consume more fiber foods like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables.
- Prepare Food at Home: Plan your meals so as not to have too much added sugar in baked products and sauces.
- Be mindful of labeling: Read the labels of all packaged foods, even snacks, sauces, and drinks, and be aware of any hidden sugars.
Eat less sugar, less of the inevitable overindulgence in sweet "comfort" foods, by eating mindfully which means eating slowly and truly enjoying your meals.
Can I reduce sugar levels with any supplement?
Yes, you can reduce your sugar levels by using Dia control tablets to effectively reduce sugar levels in your body. Check out the benefits of these top-quality supplements and experience how they can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels and support overall well-being.
Benefits of Dia control Supplement
1. Helps in Weight Management: Dia control helps you achieve your weight management objectives and lessens fat storage by increasing your metabolism and regulating blood sugar levels.
2. This raises your body's sensitivity to insulin. It makes glucose to be readily absorbed by your cells and hence, to be used as fuel.
3. Keep the Blood Sugar Healthy: Dia control supplements maintain blood sugar levels within a relatively safe range to avoid dangerous fluctuations or spikes.
4. Develops Digestive Health: By enhancing nutrition absorption and encouraging gut health, this supplement helps your digestive system.
5. Improves Heart Health: Dia control tablets can lower cardiovascular risks and promote heart health by helping you maintain appropriate levels of triglycerides and cholesterol.
6. Dia control reduces inflammation in your body because it possesses anti-inflammatory properties, and this helps curb inflammation issues associated with high blood sugar levels due to diabetes.
7. Improves Your Energy Levels: As it helps to support normal blood sugar levels, Dia control ensures that your energy stays balanced throughout the day without the spikes and crashes.
8. It Boosts Up Your Metabolism: With Dia control supplements, your metabolism is increased as well so that your body can assimilate nutrients more effectively while maintaining your energy throughout the day.
Trust me, these Dia control tablets can reduce your weight and sugar levels, making you more healthy. No one will ever make fun of your weight, and you won't give them a chance to insult you.
Conclusion:
Recent studies highlight that there is an immense association between sugar intake and mental health. Risks are included, such as mood swing, anxiety, and cognitive decline, associated with excessive sugar consumption. Reducing those modern high-sugar foods and sweets in India could play the most crucial role, as most traditional diets are very rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Avoid sugary items as much as possible and embrace mindful eating practices to ensure a healthy lifestyle that finds a nice harmony between modern science and traditional wisdom.
FAQ’s:
1. Can sugar reduction enhance mental clarity?
Yes, less sugar will balance blood sugar levels, thus maintaining one's ability to focus better and enhance cognitive functions that progressively clear up mental ability.
2. What would be better alternatives to sweets?
You should choose snacks like nuts and seeds, curd, fresh fruits, which are all full of sustained energy and are packed with nutrients without any sugar rush.
3. How is sugar related to anxiety and depression?
Excess sugar causes blood sugar swings and inflammation, thereby disturbing the brain chemistry, and can provoke or even exacerbate anxiety and depressive symptoms.
No comments





















0 comments